Macro Economic Issues (II)

National Income
Meaning: National income means the value of goods and services produced by the country during a financial year. Thus, it is the net result of all economics activities of any country during a period of one year and is valued in terms of money. National income is an uncertain term and is often used interchangeably with the national dividend, national output and national expenditure.
Definition: According to Marshall “The labor and capital of a country acting on its natural resources produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial including services of all kinds.
For example, a product runs in the supply from the producer to distributor to wholesaler to retailer and then to the ultimate consumer. If on every movement commodity is taken into consideration then the value of National Income increases.
Methods of estimating national income:
In this national income we have three methods, There are
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross National product (GNP) Net National Product (NNP)
1. GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCTS (GDP)GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period.
This definition has four parts:
Market value
Final goods and services
Produced within a country
In a given time period
Market value GDP is a market value-goods and services are valued at their market prices.
To add apples and oranges, computers and popcorn, we add the market values so we have a total value of output in rupees.
Final goods and services GDP is the value of the final goods and services produced. A final goods (or services) is an item bought by its final user during a specified time period.
A final good contrasts with an intermediate good, which is an item that is produced by one firm, bought by another firm, and used as a component of a final good or service. Excluding intermediate goods and services avoids double counting
Produced within a country
GDP measures production within a country-domestic production.
In a given time period GDP measures production during a specific time period, normally a year or a quarter of a year.
There are three different ways to measure GDP:
•Product Method
•Income Method and
•Expenditure Method.
These three methods of calculating GDP yield the same result because, National Product = National Income = National Expenditure.
1. NET DOMESTIC PRODUCTS (NDP)
GDP is aggregate money value of final goods and services produced in domestic territory of the country during an accounting year.
According to Prof. Hansen, “By gross domestic product we mean value of all the goods and services produced in any given period usually in a year in domestic territory”. GDP can be calculated by using a formula, “NDP=GDP-Depreciation charges”
2. Gross National Product (GNP)
GNP is defined as the money valve of goods and services produced in a country in a year time.
According to W.C Peterson, “Gross national product may be defined as the current market value of goods and services produced by the economy during an income period.”
While calculating GNP, the money value of only goods and services, which are finally consumed by the people are to be considered. Hence the value of all intermediary goods and inputs are to be excluded in order to avoid double counting.
3. Net National Product (NNP)
Net national product is the market value of the net output of final goods and services produced by the country during the relevant income period. In the process of production, a certain part of the GNP is to be kept aside so that worn out capital is replaced this part of the GNP is not available either for consumption or for investment purpose. Hence to deduct this replacement charges with that of GDP to get NNP. Hence, NNP=GNP-Depreciation charges
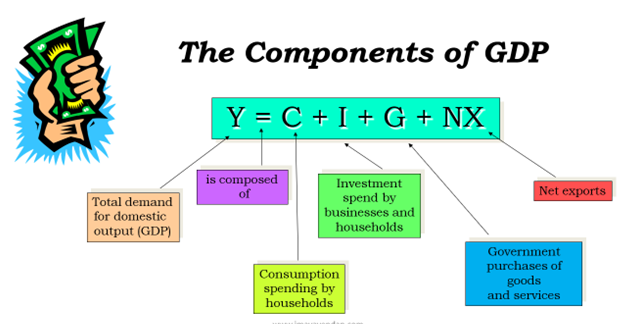
The Components of GDP
Consumption (C):The spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing.
Investment (I):The spending on capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including new housing.
Net Exports (NX):Exports minus imports
Government Purchases (G): The spending on goods and services by local, state, and federal governments.
Inter-sectoral linkages:
Introduction: The three sectors of the economy are related to one another in many ways. Agriculture depends upon industry for the supply of its inputs and implements and Industry depends on the agriculture for the demand of its products. Services are dependent upon both, hence one cannot be separated from the other in the economy.
Objectives By studying this lesson the students will be in a position to understand the inter linkage of one sector of the economy to the other. How agriculture is the back bone of the industries and in return industries are facilitators of the agriculture.
Content:
1.Agriculture as the provider of livelihood and employment in underdeveloped economy.
2.Agriculture as the supplier of raw materials to the industry.
3.Agriculture as the placer of demand for industrial goods.
4.Industries as the absorber of the labor force shifted from agriculture.
5. Industries as the provider of industrial and consumer goods to the agriculture.
6. Industries as the provider of agricultural implements to agriculture.
7. Services as the consequence of the development of these two Sectors and facilitator to them
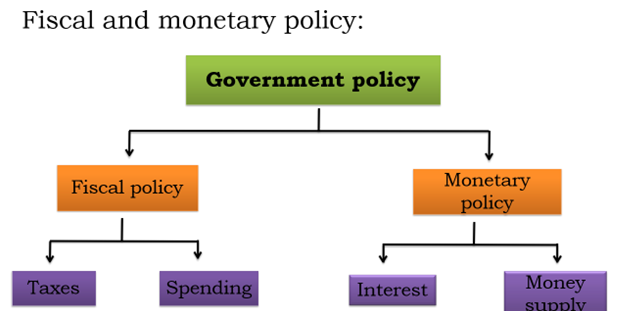

Fiscal policy:
Fiscal policy, in simple terms, is an estimate of taxation and government spending that impacts the economy. Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and tax policies to influence economic conditions, especially macroeconomic conditions, including aggregate demand for goods and services, employment, inflation, and economic growth.
Objectives of Fiscal Policy:
1.To maintain economic stability in the country
2.To bring Price stability
3.To achieve full employment
4.To provide social justice
5.To promote export and introduce import substitution
6.To mobilize more public revenue
7.To reallocate available resources To achieve balanced regional growth.
Importance of Fiscal Policy:
In a country like India, fiscal policy plays a key role in elevating the rate of capital formation both in the public and private sectors. Through taxation, the fiscal policy helps mobilize considerable amount of resources for financing its numerous projects. Fiscal policy also helps in providing stimulus to elevate the savings rate.
The fiscal policy gives adequate incentives to the private sector to expand its activities. Fiscal policy aims to minimize the imbalance in the dispersal of income and wealth.
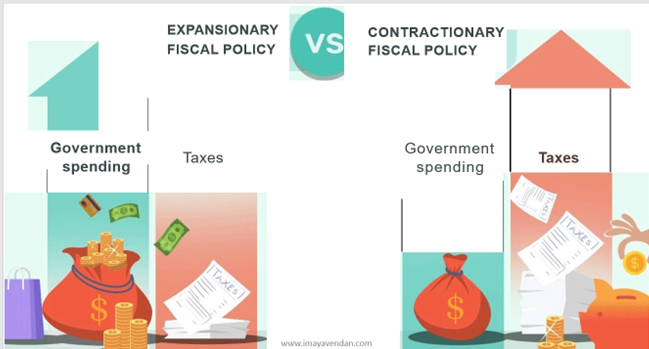
Types of policy: There are two types of fiscal policy:
Expansionary fiscal policy
Contractionary fiscal policy
Tools of fiscal policy:
There are two key tools of the fiscal policy: Taxation Government spending
Monetary Policy:
Monetary policy is an economic policy that manages the size and growth rate of the money supply in an economy. It is a powerful tool to regulate macroeconomic variables such as inflation and unemployment.
Objectives Of Monetary Policy
1.To achieve Price stability
2.To attain Exchange rate stability
3.To avoid the negative impacts of business cycle To experience full employment position
Tools of Monetary Policy
Interest rate adjustment
Change reserve requirements
Open market operations
Monetary Policy And Economic Development:
Economic development needs the support of credit planning
Improving the efficiency of banking system
Decide interest rates
Public debt management
Limitations Of Monetary Policy:
1.Monetary policy operates in a broad front
2.Success and failure depends on the banking system of the country
3.It has Institutional restrictions
4.Unorganized money market does not support the monetary policy
5.Existence of non monetized sector also defies RBI’s regulation
6.It is not very effective in overcoming depression.

Difference between Monetary and Fiscal policy
| Monetary policy | Fiscal policy | |
| Definition | It is a financial tool that is used by the central banks in regulating the flow of money and the interest rates in an economy | It is a financial tool that is used by the central government in managing tax revenues and policies related to expenditure for the benefit of the economy |
| Managed By | Central Bank of an economy | Ministry of Finance of an economy |
| Measures | It measures the interest rates applicable for lending money in the economy | It measures the capital expenditure and taxes of an economy |
| Monetary policy | Fiscal policy | |
| Focus Area | Stability of an economy | Growth of an economy |
| Impact on Exchange rates | Exchange rates improve when there is higher interest rates | It has no impact on the exchange rates |
| Targets | Monetary policy targets inflation in an economy | Fiscal policy does not have any specific target |
| Impact | Monetary policy has an impact on the borrowing in an economy | Fiscal policy has an impact on the budget deficit |
Business and Government
Government of India directly or indirectly plays a major role in assisting, encouraging and directing private sector, providing infrastructure facilities, controlling private economic activity for sustainable economic development of the country. Overall economy is regulated through fiscal, monetary policy and trade policies to participate in the globalization.
Role Of Government In India:
1.Individual freedom
2.Coexistence of public and private sector
3.Planning
4.Social welfare
Economic Environment Trough Public Private Participation (PPP)
Public Private Participation (PPP) is defined as cooperative institutional arrangements between public and private enterprise which has gained wide interest around the world.
PPP model is a new way to handle infrastructure projects.
It can benefit both the public and private sector enterprise.
The major arrangements between the public and private participation are:
1.Institutional cooperation.
2.Long term infrastructure contracts. Like construction of Roads for the public use which reduces the pressure on the exchequer, but benefits the private through way toll fee.
3.Community development
4.Urbanization and Economic development
Characteristic Features Of PPPs:
1.Cooperative and contractual relationship
2.Shared responsibilities
3.A method of procurement
4.Risk transfer
5.Flexible ownership
Economic indicators technology:
Economic indicators are key stats about the economy that can help you better understand where the economy is headed. These indicators can help investors decide when to buy or sell investments. For example, if the stock market is at its peak, you may want to sell. If the market is low and on the rise, you may want to buy.
Types of Economic Indicators
There are three types of economic indicators:
Leading
Lagging and
Coincident
Employment and poverty
Employment:
When persons are holding a job and they perform for any paid work. Also if workers hold jobs because of illness, strike or vacation, they are considered as employed.
Full Employment:
When 94-95% of them are employed or highest sustainable level of employment over the long run is called as full employment.
Under Employment: Less than full employment is called as under employment.
Unemployment: When people are not working and are actively looking for work or waiting to return to work, such a situation may be called as unemployment.
Types Of Unemployment
1.Frictional unemployment
2.Structural unemployment
3.Cyclical unemployment
4.Technological unemployment
5.Seasonal unemployment
6.Disguised unemployment
Money Market
The money market refers to trading in very short-term debt investments. At the wholesale level, it involves large-volume trades between institutions and traders. At the retail level, it includes money market mutual funds bought by individual investors and money market accounts opened by bank customers.
Examples of Money Market Instrument Banker’s Acceptance
Treasury Bills
Repurchase Agreements
Certificate of Deposits
Commercial Papers
Functions of Money Market Instruments
Provides Funds
Use of Surplus Funds
No need to borrow from banks
Helps Government
Helps in Monetary Policy
Helps in Financial Mobility
Promotes Liquidity and Safety
Equilibrium between Demand and Supply of Funds
Economy in Use of Cash
Instruments of the Money Market
Promissory Note
Bills of exchange or commercial bills
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
Call and Notice Money
Inter-bank Term Market
Commercial Papers (CPs)
Certificate of Deposits ( CD’s )
Banker’s Acceptance (BA)
Repurchase Agreements (Repo)
Capital market: Capital markets are the exchange system platform that transfers capital from investors who want to employ their excess capital to businesses that require the capital to finance various projects or investments.
Types of Capital Markets
There are two types of capital market:
Primary Market
Secondary Market
Primary Market:
Origination
Underwriting
Distribution
Secondary Market:
Regular information about the value of security
Offers liquidity to the investors for their assets
Continuous and active trading
Provide a Market Place
